 07-fetch获取数据
07-fetch获取数据
原文链接:https://nextjs.org/learn/dashboard-app/fetching-data (opens new window)
现在您已经创建并初始化了数据库。让我们讨论一下为应用程序获取数据的不同方法,并构建您的仪表板概览页面。
# 本章目标
- 了解一些获取数据的方法:APIs, ORMs, SQL, etc.
- 服务器组件如何帮助您更安全地访问后端资源
waterfalls是什么样的网络- 如何使用JavaScript模式实现并行数据提取
# 选择如何获取数据
# API层
API是应用程序代码和数据库之间的中间层。在以下几种情况下,您可能会使用API:
- 如果您使用的是提供API的第三方服务。
- 如果要从客户端获取数据,您希望在服务器上运行一个API层,以避免将数据库密码暴露给客户端。
在Next.js中,您可以使用路由处理程序 (opens new window)创建API端点。
# 数据库查询
当您创建一个全栈应用程序时,您还需要编写与数据库交互的逻辑。对于像Postgres这样的关系数据库 (opens new window),您可以使用SQL或ORM (opens new window)来实现这一点。 在一些情况下,您必须编写数据库查询:
- 在创建API端点时,您需要编写逻辑来与数据库交互。
- 如果您正在使用React Server Components(在服务器上获取数据),您可以跳过API层,并直接查询您的数据库,而不会冒着将数据库密码暴露给客户端的风险。
让我们进一步了解React服务器组件。
# 使用react server组件获取数据
默认情况下,Next.js应用程序使用React server组件。使用服务器组件获取数据是一种相对较新的方法,使用它们有一些好处:
- 服务器组件支持使用promise,为异步任务(如数据提取)提供更简单的解决方案。您可以使用async/await语法,而无需访问useEffect、useState或数据获取库。
- React server组件在服务器上执行,因此,您可以在服务器上保留昂贵的数据获取和逻辑,只将结果发送给客户端。
- 如前所述,由于React server组件在服务器上执行。您可以直接查询数据库,而不需要额外的API层。
# 使用SQL
对于您的仪表板项目,您将使用Vercel Postgres SDK (opens new window)和SQL编写数据库查询。我们将使用SQL的原因有几个:
- SQL是查询关系数据库的行业标准(例如ORM在后台生成SQL)
- 对SQL有一个基本的了解可以帮助您理解关系数据库的基本原理,从而将您的知识应用于其他工具。
- SQL是通用的,允许您获取和操作特定的数据。
- Vercel Postgres SDK提供针对SQL注入 (opens new window)的保护。
如果您以前没有使用过SQL,请不要担心,我们已经为您提供了查询。
转到/app/lib/data.ts文件,在这里你会看到我们正在从@vercel/postgres导入sql函数。此功能允许您查询数据库:
import { sql } from '@vercel/postgres';
// ...
2
3
您可以在任何服务器组件内部调用sql。但为了让您更容易地浏览组件,我们已经将所有的数据查询保存在data.ts文件中,您可以将它们导入到组件中。
注意:如果您在第6章中使用了自己的数据库提供程序,则需要更新数据库查询才能使用您的提供程序。您可以在/app/lib/data.ts中找到查询。
# 获取仪表板概述页的数据
dashboard overview页面数据。
现在您已经了解了获取数据的不同方法,让我们为仪表板概述页面获取数据。导航到/app/dashboard/page.tsx,粘贴以下代码,并花一些时间进行探索:
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
export default async function Page() {
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
{/* <Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" /> */}
{/* <Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" /> */}
{/* <Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" /> */}
{/* <Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/> */}
</div>
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
{/* <RevenueChart revenue={revenue} /> */}
{/* <LatestInvoices latestInvoices={latestInvoices} /> */}
</div>
</main>
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
在上面的代码中:
- Page是一个异步组件。这允许您使用
await来获取数据。 - 还有3个组件接收数据:
<Card>、<RevenueChart>和<LatestInvoices>。它们当前已被注释掉,以防止应用程序出错。
# 获取 RevenueChart 组件数据
为<RevenueChart/>组件获取数据。从data.ts导入fetchRevenue函数,并在组件内部调用它:修改第5行和第8行代码
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchRevenue } from '@/app/lib/data';
export default async function Page() {
const revenue = await fetchRevenue();
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
然后,取消注释<RevenueChart/>组件,导航到组件文件(/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart.tsx);并取消注释其中的代码。检查 localhost,您应该能够看到使用收入数据的图表。
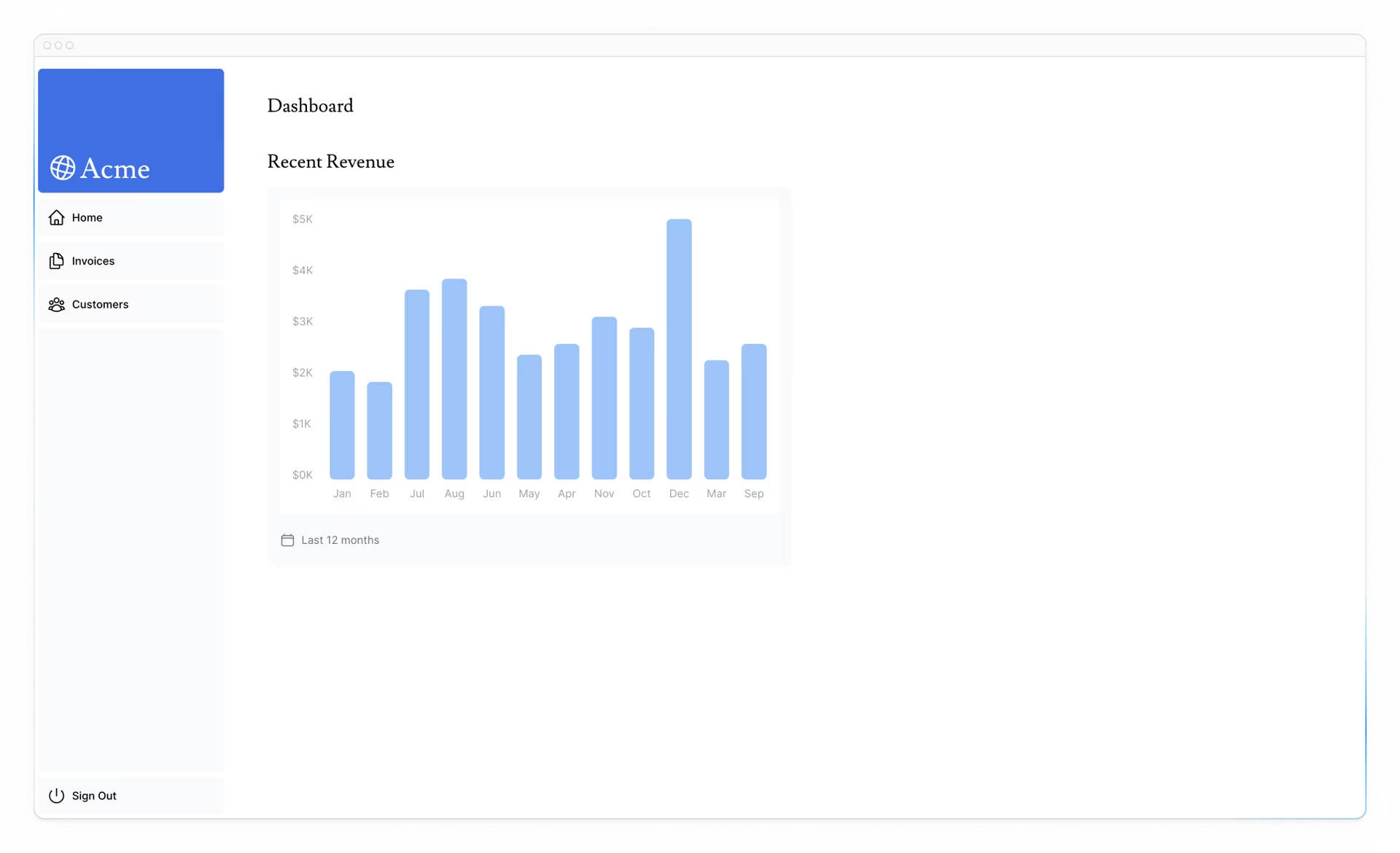 让我们继续导入更多的数据查询!
让我们继续导入更多的数据查询!
# 获取 LatestInvoices 组件数据
对于<LatestInvoices/>组件,我们需要获得按日期排序的最新5张发票。
您可以获取所有invoices并使用JavaScript对其进行排序。这不是问题,因为我们的数据很小,但随着应用程序的增长,它可以显著增加每次请求传输的数据量以及对其进行排序所需的JavaScript。
代替用排序获取最新的5条数据,您可以使用SQL查询只获取最后5个invoices。例如,这是来自data.ts文件的SQL查询:
// Fetch the last 5 invoices, sorted by date
const data = await sql<LatestInvoiceRaw>`
SELECT invoices.amount, customers.name, customers.image_url, customers.email
FROM invoices
JOIN customers ON invoices.customer_id = customers.id
ORDER BY invoices.date DESC
LIMIT 5`;
2
3
4
5
6
7
在您的页面中,导入fetchLatestInvoices函数:
修改第5行和第9行
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import { fetchRevenue, fetchLatestInvoices } from '@/app/lib/data';
export default async function Page() {
const revenue = await fetchRevenue();
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
然后,取消对<LatestInvoices/>组件的注释。您还需要取消注释<LatestInvoices/>组件本身中的相关代码,位于文件/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices中。
如果您访问localhost,您应该会看到数据库只返回最后5个。希望您开始看到直接查询数据库的优势!
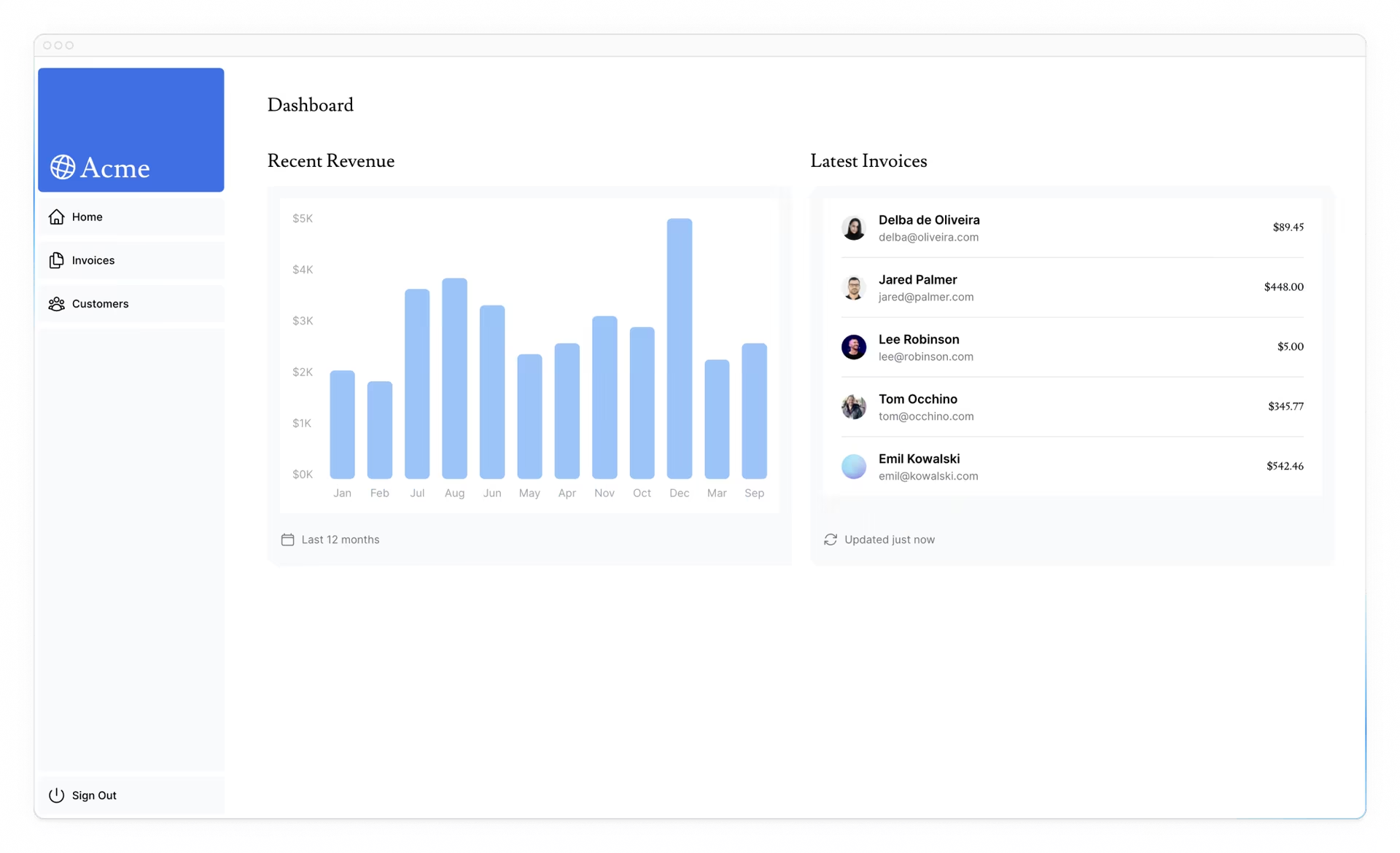
# 获取Card组件数据
现在轮到您为<Card>组件获取数据。卡片将显示以下数据:
- 已完成支付的invoices的总量
- 支付中的invoices的总量
- invoices的总量
- customers的总量
同样,你可能会被诱惑去获取所有的invoices和customers,并使用JavaScript来处理数据。例如,您可以使用Array.length来获取invoices和customers的总数:
const totalInvoices = allInvoices.length;
const totalCustomers = allCustomers.length;
2
但是使用SQL,你只能获取你需要的数据,它是一个比Array.length更小的数据。这意味着在请求期间需要传输的数据更少。这是SQL备选方案:
const invoiceCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM invoices`;
const customerCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM customers`;
2
您需要导入的函数称为fetchCardData;您将需要销毁从函数返回的值。
提示:
- 检查卡组件,查看它们需要什么数据
- 检查data.ts文件以查看函数返回的内容。
准备好后,查看最终代码:
import { Card } from '@/app/ui/dashboard/cards';
import RevenueChart from '@/app/ui/dashboard/revenue-chart';
import LatestInvoices from '@/app/ui/dashboard/latest-invoices';
import { lusitana } from '@/app/ui/fonts';
import {
fetchRevenue,
fetchLatestInvoices,
fetchCardData,
} from '@/app/lib/data';
export default async function Page() {
const revenue = await fetchRevenue();
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices();
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData();
return (
<main>
<h1 className={`${lusitana.className} mb-4 text-xl md:text-2xl`}>
Dashboard
</h1>
<div className="grid gap-6 sm:grid-cols-2 lg:grid-cols-4">
<Card title="Collected" value={totalPaidInvoices} type="collected" />
<Card title="Pending" value={totalPendingInvoices} type="pending" />
<Card title="Total Invoices" value={numberOfInvoices} type="invoices" />
<Card
title="Total Customers"
value={numberOfCustomers}
type="customers"
/>
</div>
<div className="mt-6 grid grid-cols-1 gap-6 md:grid-cols-4 lg:grid-cols-8">
<RevenueChart revenue={revenue} />
<LatestInvoices latestInvoices={latestInvoices} />
</div>
</main>
);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
太棒了现在,您已经获取了仪表板概述页面的所有数据。您的页面应该如下所示:
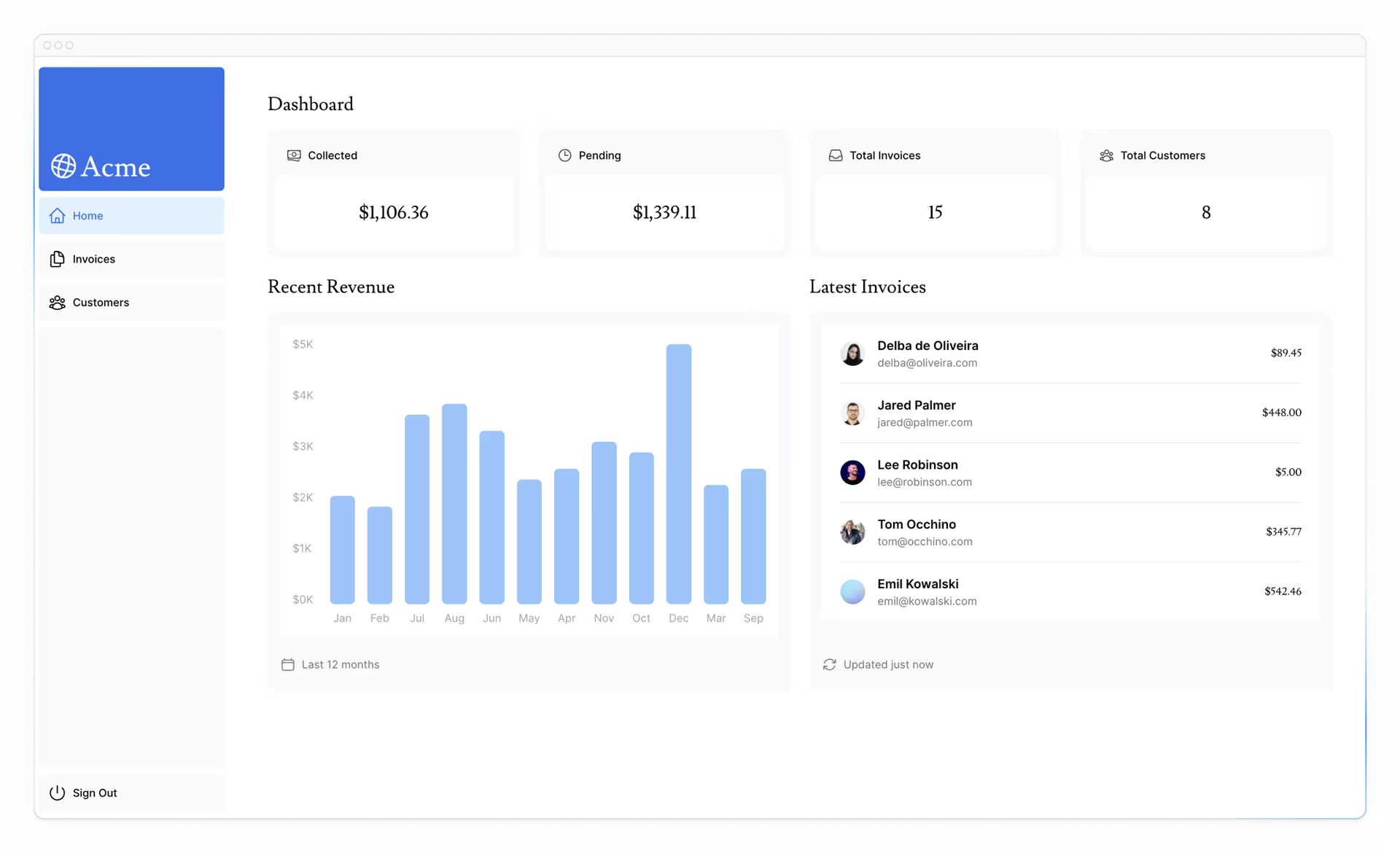 然而您需要注意两件事:
然而您需要注意两件事:
- 数据请求无意中相互阻塞,从而创建了一个请求瀑布。
- 默认情况下,Next.js预渲染路由以提高性能,这被称为静态渲染。因此,如果您的数据发生更改,它将不会反映在您的仪表板中。
# 什么是请求waterfall?
“瀑布”是指一系列网络请求,这些请求取决于先前请求的完成情况。在数据提取的情况下,每个请求只能在前一个请求返回数据后开始。
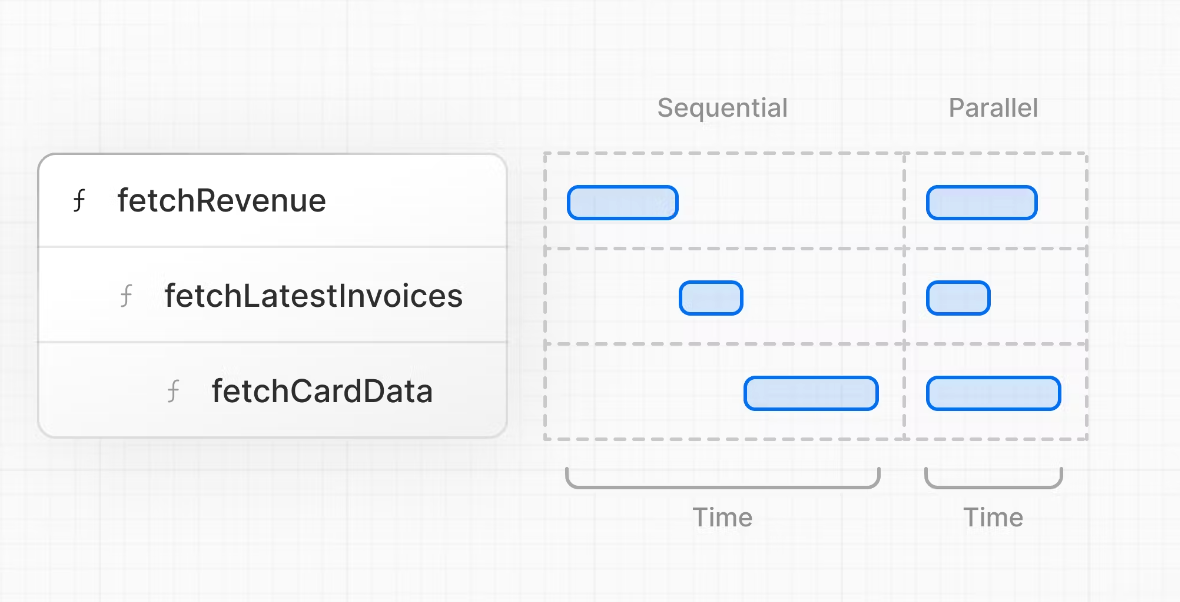 例如,在执行
例如,在执行fetchLatestInvoices()运行之前,我们需要等待fetchRevenue()完成,等等。
const revenue = await fetchRevenue();
const latestInvoices = await fetchLatestInvoices(); // wait for fetchRevenue() to finish
const {
numberOfInvoices,
numberOfCustomers,
totalPaidInvoices,
totalPendingInvoices,
} = await fetchCardData(); // wait for fetchLatestInvoices() to finish
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这种模式并不一定是糟糕的。在某些情况下,您希望在获取下一个请求之前先满足某个条件。例如,您可能希望首先获取用户的ID和配置文件信息。一旦你有了ID,你就可以继续获取他们的朋友列表。在这种情况下,每个请求都取决于从上一个请求返回的数据。 但是,这种行为也可能是无意的,会影响性能。
# 并行获取数据
避免waterfall的一种常见方法是同时启动所有数据请求——并行获取数据。
在JavaScript中,您可以使用Promise.all()或Promise.allSettled()函数同时启动所有Promise。例如,在data.ts中,我们在fetchCardData()函数中使用Promise.all():
export async function fetchCardData() {
try {
const invoiceCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM invoices`;
const customerCountPromise = sql`SELECT COUNT(*) FROM customers`;
const invoiceStatusPromise = sql`SELECT
SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'paid' THEN amount ELSE 0 END) AS "paid",
SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'pending' THEN amount ELSE 0 END) AS "pending"
FROM invoices`;
const data = await Promise.all([
invoiceCountPromise,
customerCountPromise,
invoiceStatusPromise,
]);
// ...
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
通过使用此模式,您可以:
- 同时开始执行所有数据提取,这可以提高性能。
- 使用可应用于任何库或框架的本地JavaScript模式。
然而,只依赖这种JavaScript模式有一个缺点:如果一个数据请求比其他所有数据请求都慢,会发生什么?